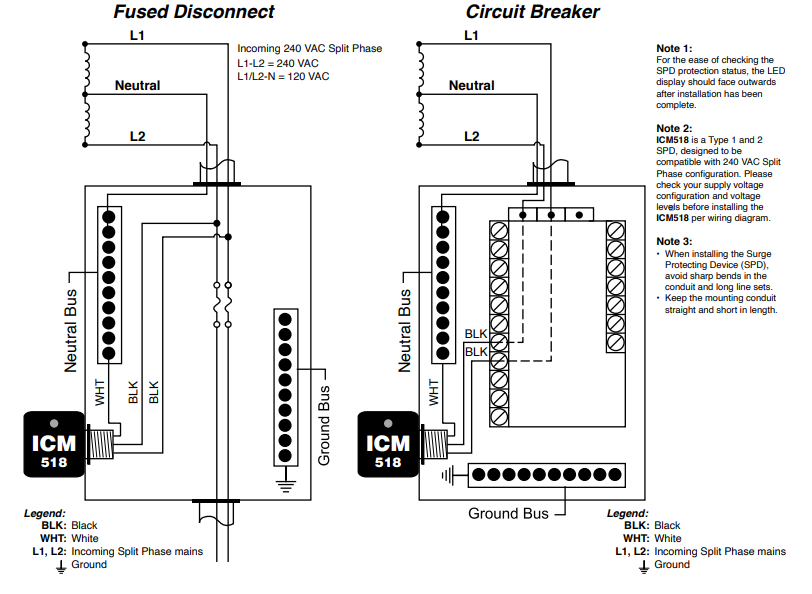
Circuit breakers and surge protectors are both electrical devices designed to protect electrical systems and appliances from damage due to power surges and electrical faults. While they may seem similar in function, they serve different purposes and operate in different ways.
Circuit Breakers
A circuit breaker is an electrical switch that automatically interrupts the flow of electricity in a circuit when it detects an overload or short circuit. When too much current flows through a circuit, the breaker trips and interrupts the flow of electricity to prevent further damage to the electrical system or the appliance or fire hazards. For example, when a 15-amp circuit has 20 amps flowing through it, eventually the circuit breaker will ‘trip’ (cut off the flow of electricity). Tripping the breaker prevents wires from overheating and igniting wire’s insulation.
Circuit breakers are an essential safety feature of modern electrical systems and are required by building codes and electrical safety standards. Their one main job is to keep the wiring inside your home or business from starting a fire.
Surge Protection Devices (SPDs)
On the other hand, a surge protector is a device that protects electrical equipment from voltage spikes and surges. Voltage surges can be caused by lightning strikes, power outages, or other events that cause a sudden increase in voltage. Voltage surges can damage or destroy sensitive electronics, such as computers, televisions, and other electronic equipment and also decrease their lifespan.
Surge protectors are designed to divert the excess voltage to ground, protecting the electrical system and equipment from damage. Surge protectors come in various forms, including power strips with built-in surge protection and whole-house surge protectors that are installed at the main electrical panel.
It’s important to note that not all surge protectors are created equal, and some may offer better protection than others. When selecting a surge protector, it’s important to consider its rating, clamping voltage, and response time to ensure that it provides adequate protection for your specific devices and needs.
While many people have point-of-use surge protector strips on televisions, computers, and gaming equipment, most people forget about protecting larger appliances like their HVAC system, freezer, or pool system. The most effective solution is a whole house surge arrester that protects the circuits directly at the electrical panel, modulating and controlling your home’s power.
A whole-home surge protector is a device that’s installed in your electric circuit breaker box or main point of power entry to your home. A surge arrester will help protect your electronics from internal and external power surges. Most electronic devices are rated for 120 volts, but a major lightning strike creates an electromagnetic pulse that can send millions of volts into a building or home’s electrical panel, wiring system, and connected devices, frying them instantly.
A circuit breaker can help prevent damage to your electrical system in the event of an overload or short circuit, but unfortunately, it is not designed to protect against power surges. By installing surge protection devices at the main electrical panel and at individual outlets or power strips, you can help safeguard your valuable electronics and appliances from the damaging effects of power surges. Using circuit breakers in conjunction with surge protectors provides two-fold protection for electrical systems and devices. Circuit breakers can prevent overloading and short circuits, while surge protectors can prevent damage caused by voltage spikes or surges.
In conclusion, circuit breakers and surge protectors are both essential components of modern electrical systems. While they may seem similar in function, they serve different purposes and operate differently. Circuit breakers protect against overloads and short circuits, while surge protectors protect against voltage spikes and surges. Understanding the differences between these devices can help homeowners and businesses protect their electrical systems and appliances from damage and downtime.